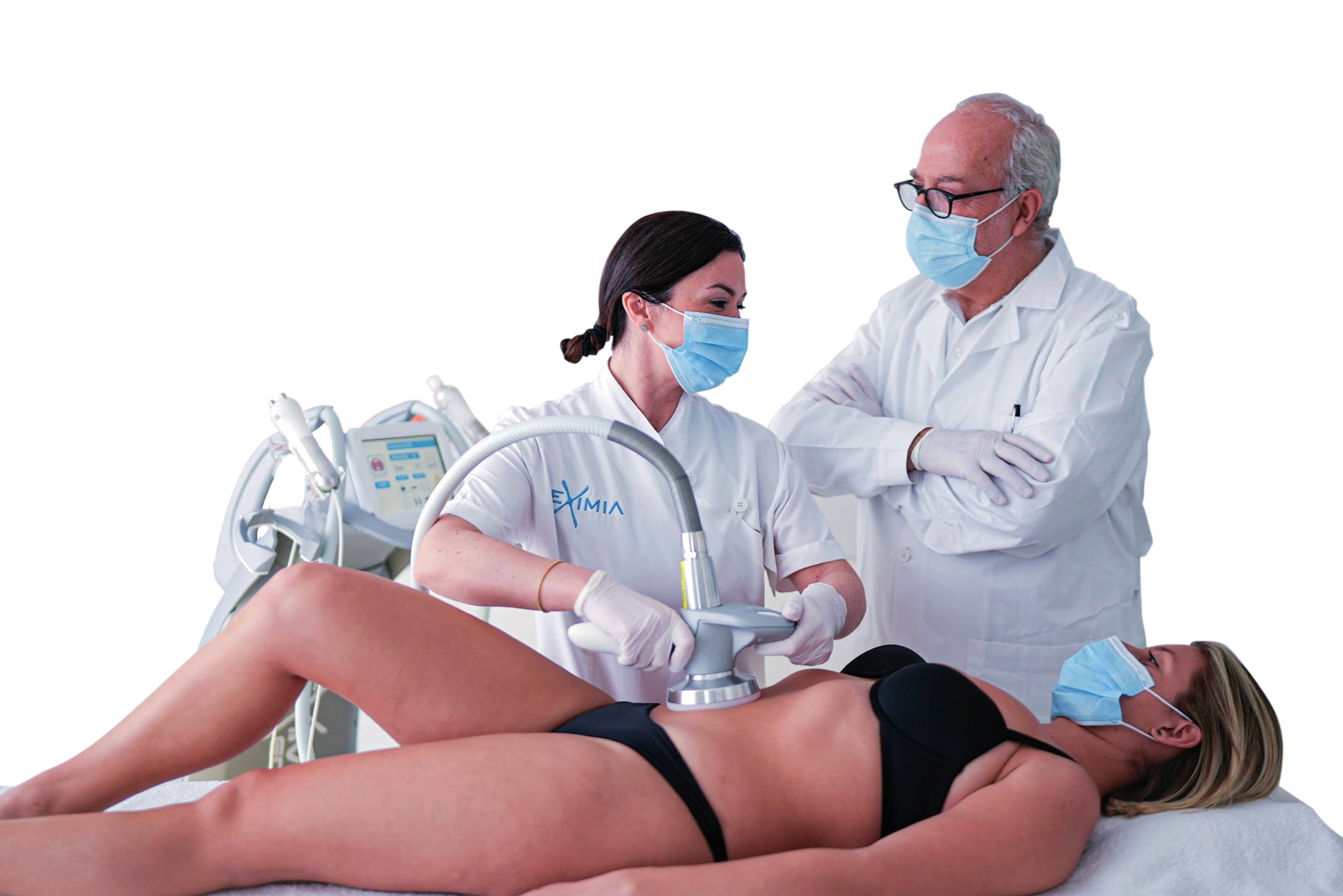

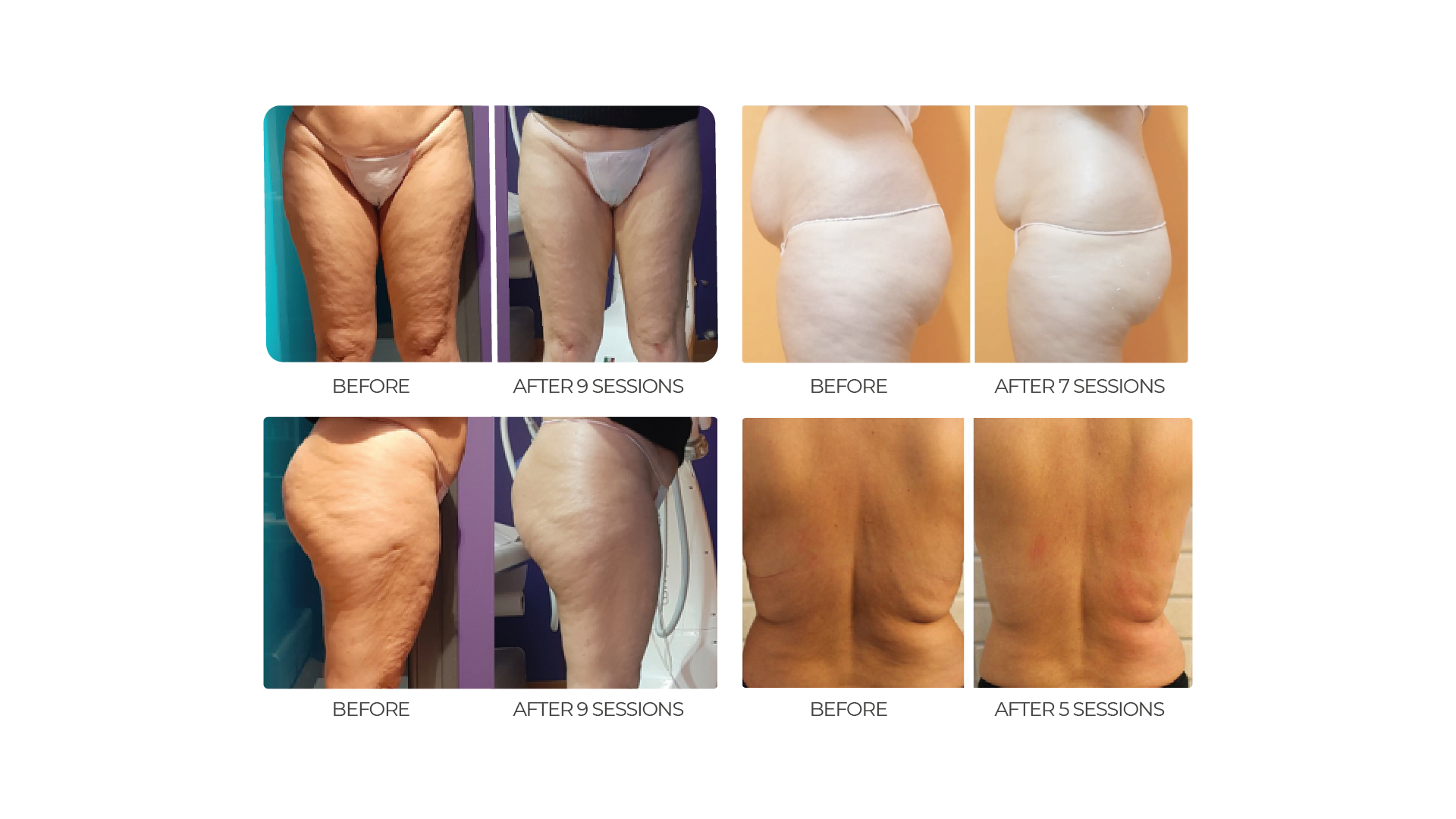
EximiaMed 7.0 offers the latest technologies for highly qualitative, safe and efficient medical protocols, a unique smart reference for body contouring and non-invasive dermal regeneration.

Gynoid lipodystrophy (or sclerotic fibrous edematous panniculopathy, commonly called "cellulite") is an inflammatory structural disease of the subcutaneous tissue that causes alterations in the skin topography. These changes result from protrusions and depressions of the skin, mainly located in the buttocks, lower limbs, and abdomen.
Cellulite occurs in approximately 90% of adult women. It can begin immediately after puberty, but is more evident in women over 30; men rarely manifest it. The etiopathogenesis of this disease has not yet been identified. Among the various hypotheses there are:
The evaluation of cellulite is fundamental both to determine the best treatment and to correctly monitor the results.
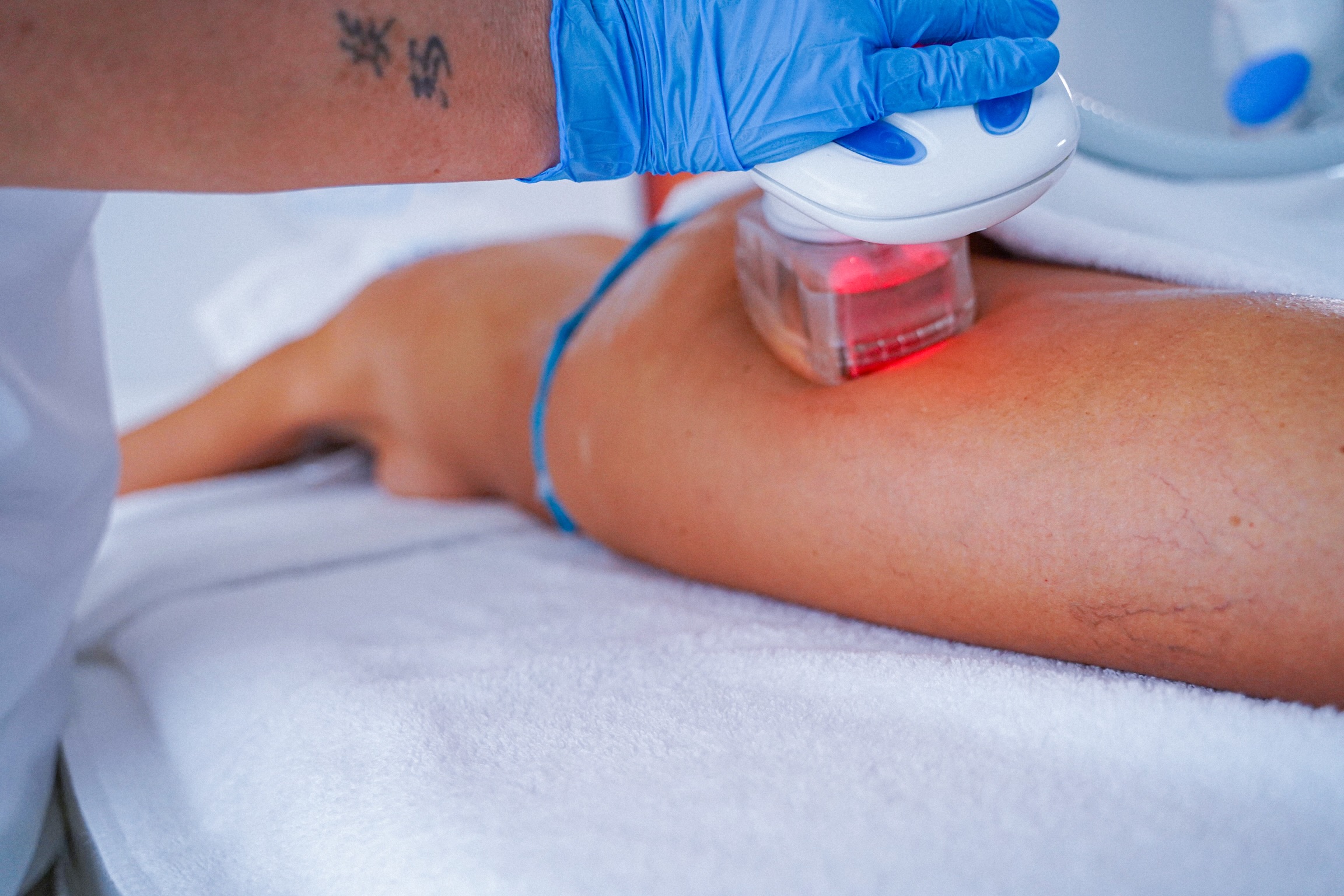
One of the techniques used for the treatment of gynoid lipodystrophy is V.L.E.P., as therapies based on the use of radio frequency (M.P.R.F. - R.F.E.P) effectively fight against the cellulite.
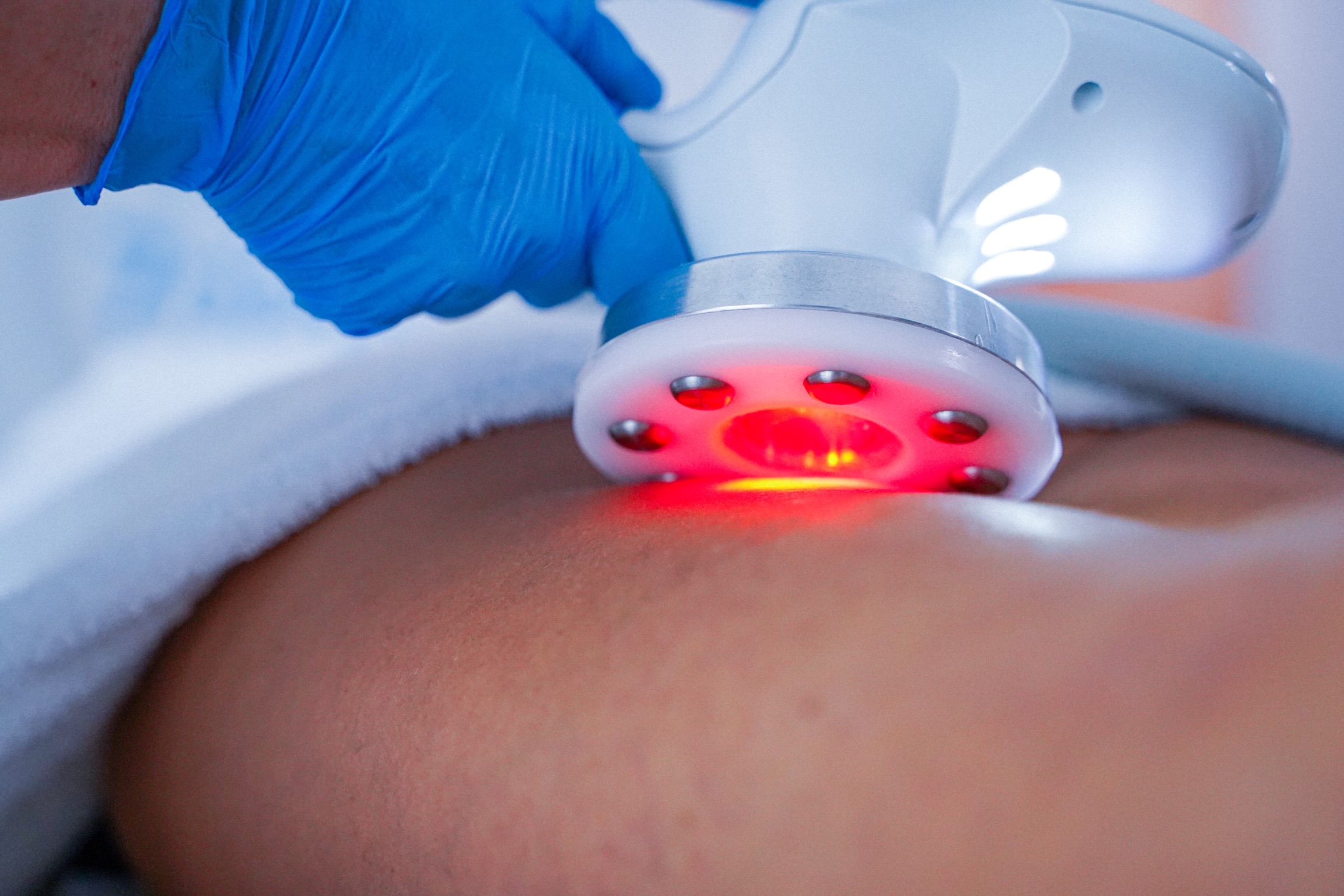
Lymphedema means a chronic and progressive condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluids, rich in proteins within the interstitial space.
The lymphatic system (whether it is the transport of vessels, nodes, interstites, etc. or combinations) falls below the capacity necessary to manage the load of microvascular filtrate, including plasma proteins and cells that escape from the bloodstream to end up in the interstice. The inflammation is produced by the accumulation in the extracellular space of excess water, filtered / diffused plasma proteins, extra-vascular blood cells and parenchymal / stromal cellular products. This process culminates in the proliferation of parenchymal and stromal elements with excessive deposition of extracellular matrix substances and adipose tissue.
One of the techniques used for the treatment of lymphedema is M.P.R.F.